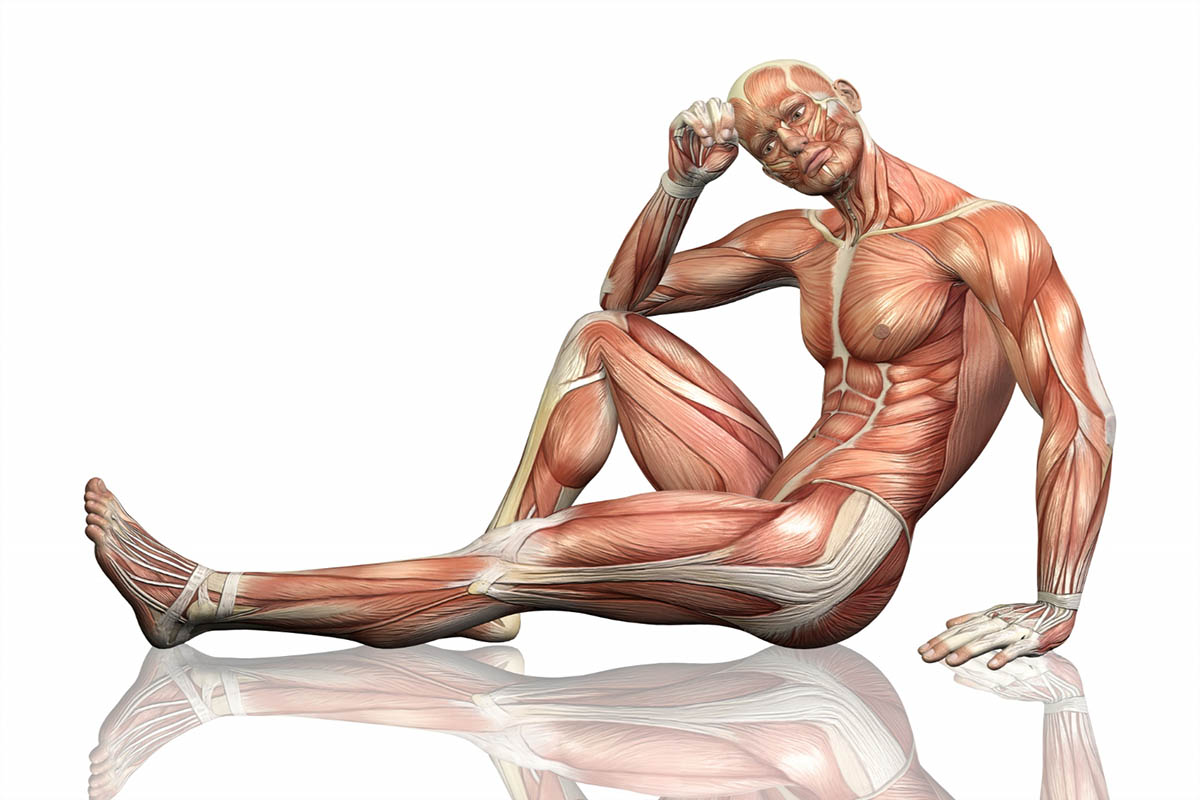
The lumbar region, often referred to as the lower back, is a critical area of the spine that plays a pivotal role in human movement and stability. Lumbar muscles, in particular, are essential components of this region, providing support, flexibility, and power for various activities. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the world of lumbar muscles. We will explore their anatomy, functions, common issues, and practical tips for maintaining lumbar muscle health. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, an athlete, or someone interested in understanding the lower back, this article will provide you with valuable insights.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Anatomy of the Lumbar Muscles
- Functions of Lumbar Muscles
- Common Lumbar Muscle Issues
- a. Lower Back Pain
- b. Muscle Strains
- c. Herniated Discs
- d. Sciatica
- Diagnosis and Assessment
- Treatment and Rehabilitation
- a. Physical Therapy
- b. Medications and Injections
- c. Lifestyle Modifications
- d. Surgery
- Preventing Lumbar Muscle Issues
- a. Exercise and Strength Training
- b. Proper Posture and Body Mechanics
- c. Ergonomics
- d. Nutrition and Hydration
- e. Stress Management
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
The lumbar muscles are the workhorses of your lower back, providing stability, mobility, and power for countless daily activities. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and the potential issues that can arise is crucial for maintaining a healthy and pain-free lower back. Whether you’re an athlete, a healthcare professional, or someone who’s experienced lower back discomfort, this article will provide a comprehensive guide to lumbar muscles.
2. Anatomy of the Lumbar Muscles
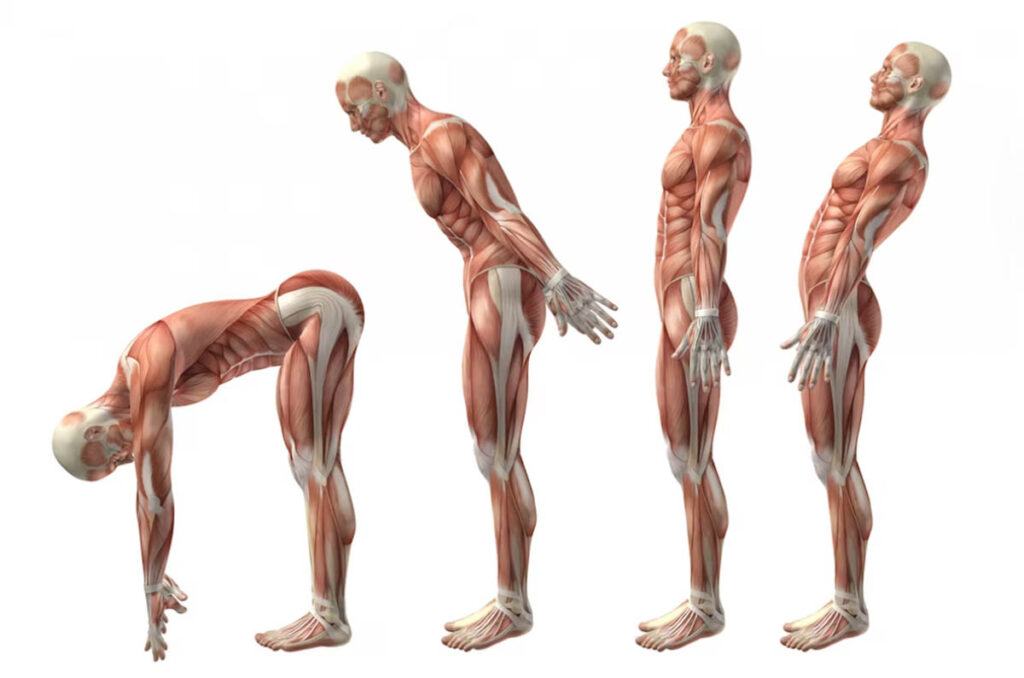
Before we delve into the functions and issues related to lumbar muscles, it’s essential to understand their anatomy. The lumbar muscles include several distinct muscle groups:
- Erector Spinae Muscles: These muscles run along the length of the spine and are responsible for maintaining an erect posture. They consist of the iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis muscles.
- Quadratus Lumborum: Located on both sides of the lower back, these muscles help with side bending and stabilizing the spine during activities like lifting.
- Multifidus: Deep muscles that run along the spine and provide stability and support for individual vertebrae.
- Psoas Major: A muscle that connects the lumbar spine to the femur and is involved in hip flexion and trunk stabilization.
- Transversus Abdominis: Part of the abdominal muscles, this muscle group plays a crucial role in core stability, which supports the lower back.
3. Functions of Lumbar Muscles
The lumbar muscles serve several vital functions in the human body:
a. Support and Stability
The erector spinae muscles, multifidus, and quadratus lumborum work together to maintain an upright posture, stabilize the spine, and prevent excessive movement during various activities.
b. Movement and Flexibility
These muscles facilitate movements such as bending forward, backward, and to the sides, as well as twisting and rotating the trunk. They are crucial for activities like lifting, twisting, and maintaining balance.
c. Core Support
The transversus abdominis, along with other core muscles, plays a significant role in providing support to the lumbar spine and maintaining core stability. A strong core helps protect the lower back during movements and activities.
4. Common Lumbar Muscle Issues
Unfortunately, lumbar muscle issues are prevalent and can lead to various symptoms and conditions. Let’s explore some of the most common problems:
a. Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain is a widespread issue that can result from muscle strains, overuse, poor posture, or underlying conditions like arthritis.
b. Muscle Strains
Strains in the lumbar muscles can occur due to overexertion, improper lifting techniques, or sudden movements. These strains can cause pain and limited mobility.
c. Herniated Discs
When the soft discs between the vertebrae in the lumbar spine herniate or bulge, they can put pressure on nearby nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower back and legs.
d. Sciatica
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the back of each leg, becomes compressed or irritated. This can lead to radiating pain, tingling, or numbness in the buttocks and legs.
5. Diagnosis and Assessment
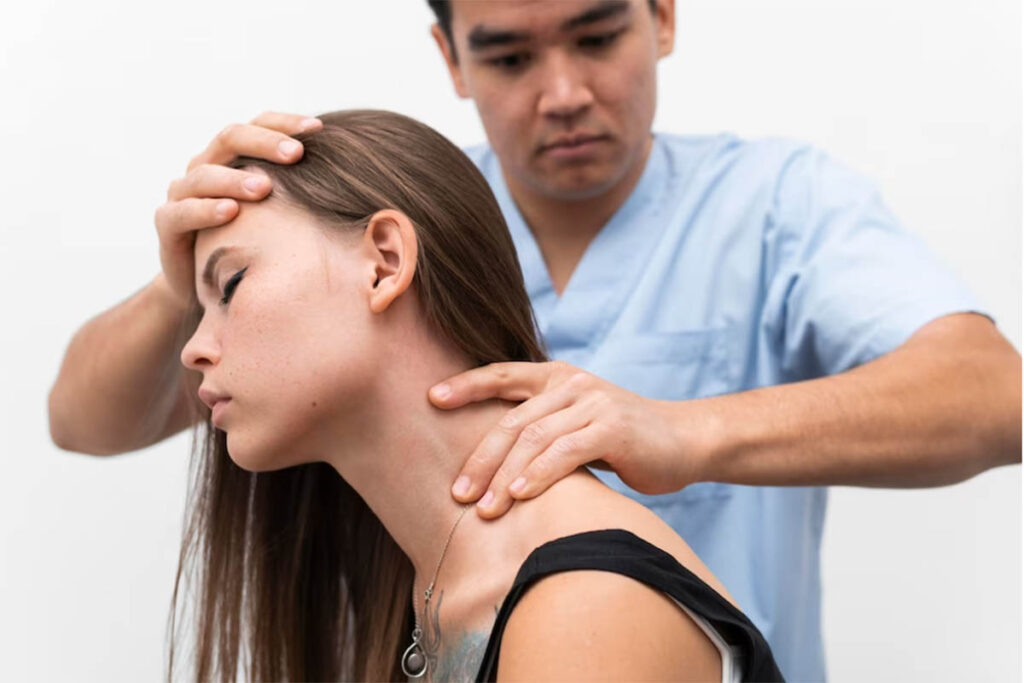
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effectively addressing lumbar muscle issues. Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose the underlying cause of lower back pain:
a. Clinical Examination
A thorough physical examination involves assessing pain location, range of motion, strength, and specific tests to identify the source of pain.
b. Imaging Studies
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans provide detailed images of the lumbar spine and surrounding structures, helping to identify issues like herniated discs or structural abnormalities.
c. Nerve Conduction Tests
In cases where nerve-related issues like sciatica are suspected, nerve conduction studies may be conducted to assess nerve function and identify areas of compression or irritation.
6. Treatment and Rehabilitation
Treatment options for lumbar muscle issues vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common approaches:
a. Physical Therapy
Physical therapists play a crucial role in rehabilitating lumbar muscle issues. They use techniques such as:
- Strengthening Exercises: Targeting specific muscle groups to improve stability and function.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques to improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
- Modalities: Such as heat, ice, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to alleviate pain and inflammation.
b. Medications and Injections
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Prescription Medications: Stronger pain medications or muscle relaxants may be prescribed for severe pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: These injections can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation, often used for conditions like sciatica.
c. Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage and prevent lumbar muscle issues. These changes may include:
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to strengthen the core and back muscles.
- Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture during sitting, standing, and lifting to reduce strain on the lower back.
- Ergonomics: Ensuring that your workstation and daily activities are ergonomically designed to minimize stress on the lower back.
- Nutrition and Hydration: Consuming a balanced diet and staying hydrated to support overall joint health.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga, as stress can exacerbate lower back pain.
d. Surgery
In severe cases or when conservative treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions may be necessary. These may include procedures to repair herniated discs, stabilize the spine, or address structural issues.
7. Preventing Lumbar Muscle Issues
Prevention is key to maintaining healthy lumbar muscles. Here are some preventive strategies:
a. Exercise and Strength Training
Regular exercise, including specific strength and flexibility exercises, can help maintain strong core and lumbar muscles, reducing the risk of strains and injuries.
b. Proper Posture and Body Mechanics
Maintain good posture during activities like sitting, standing, and lifting. Use proper body mechanics to avoid excessive stress on the lower back.
c. Ergonomics
Ensure that your workstation and daily activities are ergonomically designed to reduce the risk of lower back strain and discomfort.
d. Nutrition and Hydration
A balanced diet and proper hydration support overall joint health, including the lumbar spine.
e. Stress Management
Practice stress-reduction techniques to minimize the negative impact of stress on the lower back. Stress can exacerbate muscle tension and pain.
8. Conclusion
Lumbar muscles are essential for maintaining an active and pain-free lifestyle. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and potential issues is crucial for effectively addressing and preventing lower back pain and discomfort. If you experience persistent or severe lumbar muscle issues, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Remember that early intervention, proper rehabilitation, and preventive measures are key to maintaining healthy lumbar muscles and a functional lower back.


