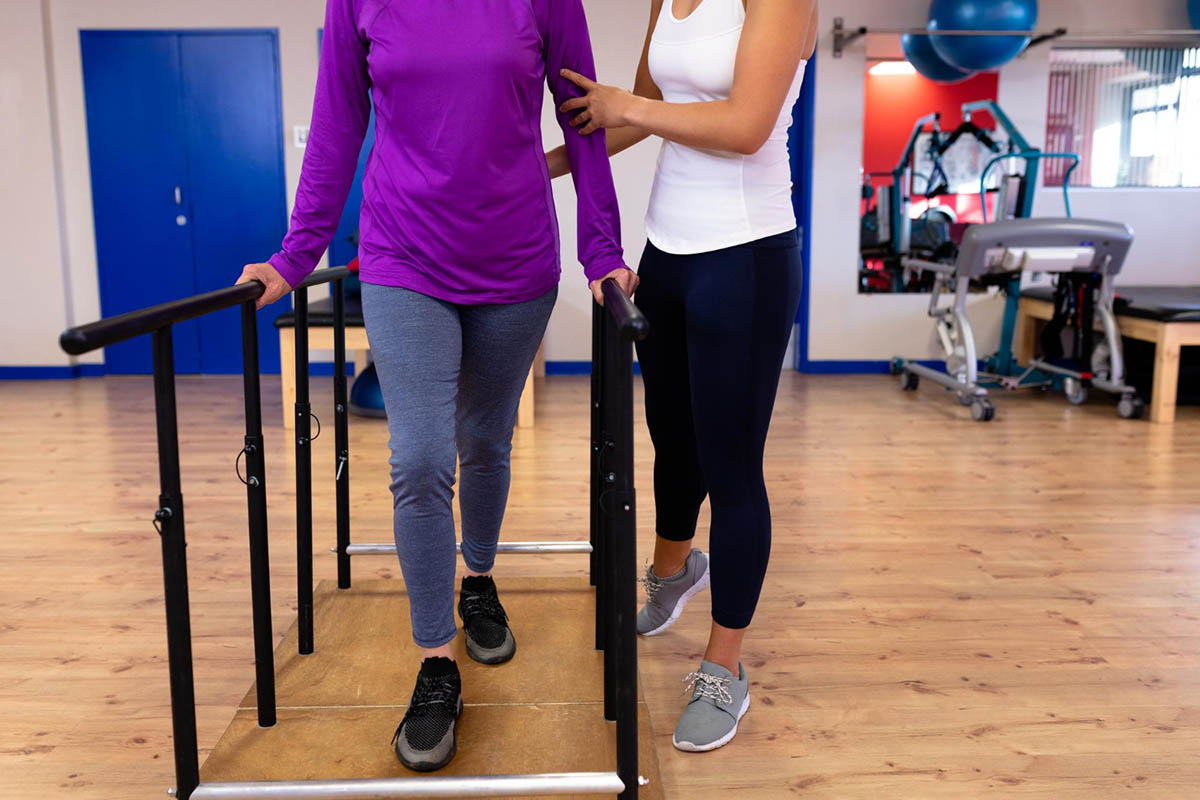
Gait training is a critical aspect of physical therapy, focusing on improving an individual’s ability to walk and move. Whether recovering from an injury, surgery, or managing a chronic condition, gait training in physical therapy helps restore a normal walking pattern and enhances mobility. Through a series of targeted gait training exercises, individuals can improve balance, muscle strength, and coordination, leading to better overall health and quality of life. In this blog, we’ll delve into what gait training in physical therapy involves, who benefits from it, and the key exercises that make up a successful gait training exercise program.
What is Gait Training in Physical Therapy?
Gait training refers to a series of therapeutic exercises aimed at improving an individual’s ability to walk. But what is gait training in physical therapy exactly? It involves evaluating a person’s walking pattern and then using specific exercises to correct or improve their movements. This type of therapy is crucial for anyone who has experienced difficulty walking due to injury, surgery, neurological disorders, or chronic pain. Understanding what is gait training in physical therapy helps patients realize how these targeted exercises improve balance, mobility, and coordination, allowing them to regain independence and quality of life.
Physical therapists use gait training to help patients restore a normal walking pattern, correct gait abnormalities, and strengthen the muscles necessary for improved mobility.
Gait training physical therapy may involve balance training, strengthening core muscles, and practicing movements that encourage proper posture and alignment. The goal is to restore normal walking patterns through therapeutic exercises and the use of biofeedback techniques to track progress. For patients recovering from a spinal cord injury, stroke, or muscle diseases, regaining control over motor functions and muscle memory is essential.
Who Benefits from Gait Training?
Many individuals with varying physical conditions benefit from gait training exercises. Patients with muscle weakness due to muscular dystrophy, joint injuries, or cerebral palsy often need assistance in regaining strength and coordination. Others recovering from limb amputations, spinal cord injuries, or stroke require gait therapy to restore gait dynamics.
In particular, patients who have suffered from abnormal gait patterns caused by neurological conditions benefit immensely from gait training. Moreover, individuals dealing with age-related balance issues, foot drop, or muscle atrophy see significant improvements in their ability to walk safely and confidently.
Athletes recovering from extremity injuries like torn ligaments or fractures also use gait training to re-establish proper movement, while older adults who are at risk for falls benefit from balance and muscle control exercises. Finally, gait training is essential for patients recovering from surgeries like hip replacements, those managing heart disease, or anyone struggling with gait dysfunction due to underlying physical conditions.
Gait abnormalities tend to become more frequent as individuals age. While approximately 15% of people develop a gait issue by the age of 60, this number significantly rises, with over 80% of individuals over the age of 85 experiencing some form of gait abnormality. For aging populations, gait training exercises physical therapy can greatly improve walking ability, reduce the risk of falls, and enhance quality of life.
Benefits of Gait Training in Physical Therapy

Improve Mobility
Gait training physical therapy restores mobility by addressing issues with muscle control, flexibility, and balance training. The exercises focus on strengthening the leg muscles, including the calf muscles, to improve overall mobility. Patients regain the ability to navigate their daily activities independently.
Research indicates that combining 30-minute sessions of high-intensity treadmill training, performed three times a week for six weeks, with conventional physical therapy, leads to more substantial improvements in both walking capacity and speed compared to standard physiotherapy alone. This approach accelerates the rehabilitation process, allowing patients to regain mobility more effectively.
Prevent and Reduce Pain
Patients with abnormal gait often experience pain due to improper weight distribution and posture. Gait training programs work to correct gait abnormalities by improving muscle tone, which helps prevent further injuries and reduces existing pain from repetitive motion or musculoskeletal disorders.
Address Gait Disorders and Conditions
Gait training exercises target conditions like spastic gait, foot drop, and muscle diseases. By correcting these issues, individuals can walk more comfortably and regain normal movement patterns over time. Physical therapy for walking helps correct gait abnormalities and assists with gait recovery in individuals who have suffered gait after stroke or other neurological conditions.
Improve Balance and Stability
Falls are a common risk for individuals with balance issues, particularly the elderly or those with neurological conditions. Balance tests and training exercises help improve stability, enabling safer walking. Enhancing balance control is key for patients recovering from stroke or spinal cord injuries.
Aid in Neurological Recovery
For those recovering from neurological injuries such as a stroke or traumatic brain injury, gait training therapy plays a crucial role in reconnecting neural pathways responsible for motor functions and movement. Exercises that engage key muscles help retrain the brain and restore a normal gait cycle.
Promote Long-Term Joint Health
By teaching proper walking mechanics, gait training exercises reduce the strain on joints, especially in patients with arthritis or joint injuries. Long-term gait therapy contributes to healthier joints and may prevent further degeneration.
How Does Physical Therapy Improve Gait?
Gait Analysis
The process starts with a comprehensive gait analysis, where physical therapists evaluate gait dynamics by observing the patient’s walking speed, posture, and foot alignment. This helps identify abnormal gait patterns that may be contributing to mobility issues.
Customizing a Gait Training Plan
Based on the analysis, therapists design a gait training program tailored to the patient’s needs. This personalized plan may include balance training, strengthening core muscles, or endurance conditioning to build up stamina for safe walking.
Gradual Progression
Progress is made gradually, with an emphasis on slow, steady improvements. Patients start from a seated position, performing small movements that target specific muscles, and advance to more complex movements as their strength and coordination improve.
Monitoring the Gait Training Journey
Throughout the process, therapists monitor the patient’s progress, adjusting the gait training exercises as needed. Gait speed measurements and balance tests help track improvements in walking speed and coordination.
Choosing the Right Assistive Device
In some cases, patients may need an adaptive device such as a cane or walker. The therapist helps select the appropriate device and provides guidance on its proper use to ensure safe walking during recovery.
Joining Group Sessions for Motivation
Many patients benefit from group sessions where they can work alongside others with similar challenges. These sessions create a supportive environment, boosting motivation and making therapy more enjoyable.
Gait Training Exercises in Physical Therapy
There are a variety of gait training exercises physical therapy professionals use to improve mobility, balance, and strength. These exercises target different muscle groups and help individuals recover from injuries or medical conditions that affect walking.
The following are some of the most common gait training exercises physical therapy clinics use to help patients recover and improve their walking patterns:
Range of Motion Exercises
These exercises improve flexibility and prepare the body for movement by enhancing the mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. Therapeutic exercises that involve muscle activity are essential for preventing stiffness and improving movement.
Lower Extremity Strengthening
Strengthening the lower extremities, especially the calf muscles, leg muscles, and core muscles, is vital for improving balance and stability. These exercises also enhance endurance, allowing patients to perform daily activities with ease.
Stepping Over Obstacles
Practicing obstacle gait training helps patients improve coordination and balance by stepping over small obstacles. This also increases muscle strength and improves the range of motion, which is particularly important for patients with extremity injuries.
Target Stepping
Target stepping involves stepping onto specific markers, which improves foot control, balance, and muscle tone. This exercise is especially useful for patients dealing with abnormal gait patterns.
Retro Walking
Retro walking or walking backward is an effective exercise that strengthens the leg muscles and enhances balance. It is often used in patients recovering from spinal cord injuries or neurological conditions.
Balance and Proprioception Exercises
These exercises focus on improving the body’s awareness of its position in space, enhancing balance and stability, and preventing falls. Strengthening the core muscles and improving coordination are key goals of proprioception exercises.
Tips for a Successful Gait Training in Physical Therapy
- Stay Consistent: Performing gait training exercises regularly ensures steady progress.
- Be Patient: Recovery takes time. Focus on small improvements and celebrate each milestone.
- Listen to Your Therapist: Following your therapist’s instructions ensures the best results and reduces the risk of further injury.
- Use Assistive Devices When Needed: If your therapist recommends an adaptive device, use it to aid in your recovery and prevent falls.
Get Expert Gait Training with Ormobility Physical Therapy & Performance

At Ormobility Physical Therapy & Performance, we specialize in personalized rehabilitation plans, including expert gait training physical therapy designed to enhance mobility, improve balance, and restore confidence in walking. Our team of experienced therapists utilizes cutting-edge techniques to address gait abnormalities and other movement-related issues. Whether you are recovering from an injury or managing a chronic condition, we also offer tailored physical therapy for balance to help you regain stability and prevent falls, ensuring a full return to daily activities with increased independence.
Conclusion
Gait training exercises play a vital role in restoring mobility, enhancing balance, and improving overall health. Whether you’re dealing with an abnormal gait, recovering from a musculoskeletal disorder, or simply want to prevent future injuries, physical therapy gait training can help you achieve your goals. Don’t hesitate to seek expert care and begin your journey toward better health and independence.
FAQ’s
Can physical therapy help with gait issues?
Yes, physical therapy is highly effective in treating gait issues. Through gait training exercises, therapists can help restore a normal walking pattern and improve overall mobility.
What is considered gait training in physical therapy?
Gait training involves specific therapeutic exercises and balance training designed to correct abnormal gait patterns and improve muscle strength and coordination.
How long does
gait training take? The duration of gait training varies depending on the medical condition and gait dysfunction. Some patients may need weeks, while others require months to see significant improvement.