Neck pain, headache, and dizziness are common complaints that affect millions of people worldwide. While these symptoms might appear unrelated at first, they are often interconnected, particularly when neck pain contributes to dizziness and headaches. This condition, known as cervicogenic dizziness, occurs when dysfunction in the cervical spine leads to balance issues, discomfort, and headaches. Understanding the link between neck pain causing headache and dizziness can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms effectively.
In some cases, conditions such as vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI), cervical artery dissection, and bow hunter’s syndrome—where blood flow to the brain is restricted due to cervical spine movement—can also lead to dizziness, headaches, and neck pain. By addressing the underlying causes through a combination of medical treatment, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce their symptoms.
Introduction to Neck Pain, Headache, and Dizziness
Neck pain and headache and dizziness are often linked to cervical spine dysfunction, which can stem from various conditions such as cervical degenerative disc disease, herniated discs, cervical stenosis, and facet joint issues. The cervical spine houses crucial structures like the cervical arteries, spinal cord, and nerve roots, all of which play a role in maintaining stability and function.
Poor posture, prolonged screen time, stress, and injury can strain the neck muscles, leading to muscle tension, inflammation, and nerve irritation. Additionally, cervicogenic dizziness may develop due to issues in the facet joints, upper cervical spine, or vertebral artery compression, further exacerbating headaches and balance problems. Identifying and treating the root cause of these symptoms is essential for long-term relief. Approaches such as physical therapy, manual therapy, vestibular rehabilitation, and even advanced interventions like platelet-rich plasma or radiofrequency ablation can help manage these symptoms effectively.
What is Cervicogenic Dizziness?
Cervicogenic dizziness is a condition where dysfunction in the cervical spine leads to dizziness, balance issues, and headaches. Unlike dizziness caused by an inner ear disorder or neurological disorder, cervicogenic dizziness is related to structural issues in the neck.
How Neck Pain Causes Dizziness and Headaches
There are several ways in which neck pain causing headache and dizziness occurs. One common cause is cervical spine dysfunction, where issues in the facet joints, intervertebral discs, or upper neck ligaments lead to pain that radiates to the head, resulting in dizziness and headaches. Another contributing factor is vertebral artery compression, as the vertebral artery runs through the cervical spine, supplying blood to the brain. When this artery becomes compressed or irritated due to poor posture, whiplash, or cervical osteoarthritis, it can disrupt blood flow, leading to dizziness and headaches. Additionally, proprioceptive dysfunction plays a significant role, as the upper cervical spine is responsible for proprioception—the body’s ability to sense movement and positioning. When there is dysfunction in the proprioceptors of the neck, it can create a mismatch in sensory information, leading to dizziness and balance issues. Understanding these mechanisms is essential in addressing the root cause of cervicogenic dizziness and finding effective treatment options.
Common Causes of Neck Pain, Headache, and Dizziness
Neck pain, headaches, and dizziness can stem from a variety of underlying conditions, ranging from structural issues in the cervical spine to poor posture and muscle imbalances. These symptoms often develop due to strain on the facet joints, intervertebral discs, and neck muscles, which can lead to nerve irritation and restricted blood flow. Understanding the most common causes can help individuals identify triggers and seek appropriate treatment before symptoms worsen.
Cervical Vertigo and Neck Pain
Cervical vertigo is a condition where dysfunction in the cervical spine affects balance and coordination, often leading to dizziness and instability. This occurs when the proprioceptors in the neck send abnormal signals to the brain, creating a mismatch in sensory input. As a result, individuals may experience unsteadiness, disorientation, or difficulty maintaining balance. Cervical vertigo is frequently associated with facet joint dysfunction, cervical muscle tension, and vertebral artery compression, making it a common cause of neck pain, headache, and dizziness.
Studies have shown that 27% of individuals with cervical vertigo experience true vertigo, 50% report headaches, and an overwhelming 94% suffer from neck pain. These findings highlight the strong link between cervical spine dysfunction and dizziness-related symptoms. Identifying and addressing the root causes of cervical vertigo through targeted therapies, including vestibular rehabilitation and physical therapy, can significantly improve symptoms and restore balance.
Cervical Headaches and Dizziness
Cervicogenic headaches originate from dysfunction in the cervical spine and are often accompanied by dizziness. These headaches are typically caused by nerve irritation, facet joint dysfunction, and spinal cord inflammation, which can lead to persistent discomfort. The pain usually starts at the base of the skull and radiates toward the forehead, often worsening with certain neck movements. In some cases, cervical radiculopathy, cervical myofascial pain syndrome, or cervical osteoarthritis may contribute to the onset of cervicogenic dizziness and headaches, making proper diagnosis and treatment essential.
Whiplash and Poor Posture
Whiplash is a sudden acceleration-deceleration injury, commonly seen in car accidents, that can severely damage the upper cervical spine. The forceful motion can strain or tear the upper neck ligaments, causing cervicogenic dizziness, headaches, and chronic neck pain. In some cases, whiplash can lead to cervical muscle atrophy, cervical stenosis, or even vertebral artery dissection, all of which may contribute to ongoing dizziness and discomfort.
On the other hand, poor posture is a gradual but equally damaging factor in the development of neck pain, headache, and dizziness. Slouching, forward head posture, and prolonged screen use place excessive strain on the levator scapula, trapezius, and scalene muscles, leading to muscle tension, nerve irritation, and poor spinal alignment. Over time, this can cause chronic pain and cervicogenic dizziness, making ergonomic adjustments and postural correction essential for prevention and long-term relief.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Treating Neck Pain and Dizziness
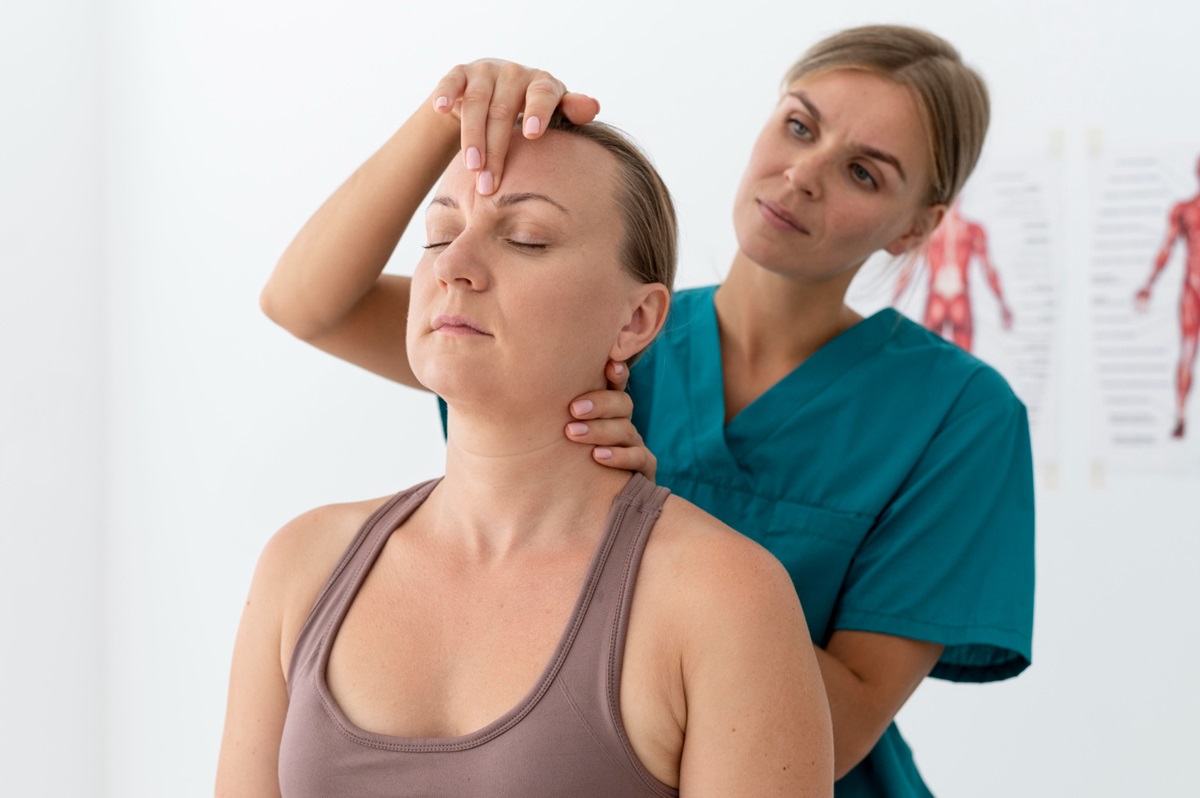
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in relieving neck pain, headache, and dizziness by addressing the root cause of discomfort rather than just managing symptoms. Through a combination of manual therapy, postural correction, and targeted exercises, physical therapy helps restore mobility, reduce muscle tension, and improve vestibular function. Whether the issue stems from whiplash, cervicogenic dizziness, or poor posture, a well-structured therapy plan can significantly enhance recovery and prevent future occurrences. OrMobility PT specializes in treating neck pain, headaches, and dizziness through personalized physical therapy programs. Our team is dedicated to identifying and addressing the root causes of your discomfort, utilizing advanced techniques to restore function and enhance your quality of life. By focusing on individualized care, we aim to help you regain control over your health without relying on expensive surgeries or medications.
How Physical Therapy Helps Relieve Dizziness
Physical therapy focuses on restoring proper function to the cervical spine, improving mobility, reducing muscle tension, and retraining the vestibular system. Vestibular rehabilitation can help individuals regain balance and prevent dizziness by improving the brain’s ability to process sensory information from the inner ear and cervical spine. Additionally, therapy sessions often include proprioception training, which enhances body awareness and stability, reducing the risk of dizziness-related falls. A personalized physical therapy plan may also incorporate chiropractic care, ergonomic adjustments, and stress management strategies to address underlying factors contributing to neck pain, headache, and dizziness.
Neck Strengthening Exercises and Posture Correction
Strengthening the multifidus, scalene muscles, and levator scapula helps stabilize the cervical spine and prevent recurrent symptoms of cervicogenic dizziness. Balance exercises and chiropractic biophysics techniques also improve posture, reducing strain on the upper cervical spine and promoting better spinal alignment. In addition, exercises focusing on the trapezius and deep neck flexors enhance support for the head and neck, helping to minimize tension and prevent imbalances that contribute to neck pain causing headache and dizziness. Regular stretching and mobility work can also prevent cervical muscle atrophy, ensuring long-term neck health and reducing the risk of future episodes of cervicogenic dizziness.
Manual Therapy and Spinal Manipulation
Techniques such as dry needling, steroid injections, and nerve blockers may provide relief by targeting trigger points and reducing muscle tension in the neck. Manual therapy, including myofascial release and spinal manipulation, helps restore proper joint movement and alleviate facet joint dysfunction, which often contributes to neck pain, headache, and dizziness. Additionally, radiofrequency ablation and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy are emerging treatments that may help with chronic neck pain by promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation. When combined with physical therapy, these interventions can improve cervical spine function and significantly enhance recovery.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Cervicogenic Dizziness
In some cases, dizziness can also be linked to head trauma, such as a concussion. The connection between dizziness and concussion is well-documented, as head injuries often cause disruptions in the vestibular system and cervical spine, leading to prolonged balance issues. Identifying the root cause of these symptoms is essential for effective treatment, and healthcare providers use a combination of clinical evaluations, medical imaging techniques, and specialized tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Identifying the root cause of these symptoms is essential for effective treatment, and healthcare providers use a combination of clinical evaluations, medical imaging techniques, and specialized tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Research suggests that cervicogenic dizziness accounts for approximately 5% of all dizziness and vertigo cases in clinical settings. In some ear, nose, and throat (ENT) clinics, non-traumatic cervicogenic dizziness has been found in 5.42% to 7.5% of patients, indicating that this condition is more prevalent than commonly recognized. Given its impact on daily life, early detection and proper management of cervicogenic dizziness are crucial for reducing discomfort and restoring functional movement.
Identifying the Link Between Neck Pain and Dizziness
Cervicogenic dizziness is often characterized by a set of distinct symptoms that help differentiate it from other causes of dizziness. Individuals with this condition frequently experience dizziness triggered by neck movement, which can occur when turning the head or maintaining a certain position for extended periods. Additionally, persistent headaches originating from the neck are a common complaint, often radiating from the base of the skull to the forehead. Other symptoms include neck stiffness, muscle tightness, and reduced mobility, making everyday activities like driving or working at a desk particularly uncomfortable. Recognizing these symptoms early can help guide individuals toward the right diagnosis and treatment for neck pain, headache, and dizziness.
Diagnostic Tests for Accurate Diagnosis
Diagnosing cervicogenic dizziness requires a comprehensive evaluation to rule out other potential causes, such as inner ear disorders or neurological conditions. Healthcare providers often rely on medical imaging techniques, including MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, to detect structural issues in the cervical spine, such as herniated discs, cervical stenosis, or facet joint dysfunction. Additionally, vestibular system testing may be performed to rule out conditions like benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) and vestibular neuritis, which can also cause dizziness. In some cases, aneurysm monitoring and screening may be necessary to check for cerebral aneurysms, ruptured aneurysms, or blood vessel wall weakening, which could contribute to dizziness and balance disturbances. By combining clinical assessments with advanced diagnostic tools, specialists can accurately identify cervicogenic dizziness and recommend the most effective treatment plan.
Prevention and Management of Neck Pain and Dizziness
Preventing neck pain, headache, and dizziness requires a proactive approach that includes maintaining good posture, strengthening the cervical spine, and making ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain on the neck. Many cases of cervicogenic dizziness are linked to poor posture, muscle tension, or cervical degenerative disc disease, all of which can be managed with lifestyle modifications and targeted therapies. By incorporating balance exercises, stress management strategies, and vestibular rehabilitation, individuals can improve their neck health and reduce the likelihood of developing chronic symptoms.
Ergonomics and Lifestyle Adjustments

Making ergonomic adjustments is crucial for preventing neck pain, headache, and dizziness, especially for individuals who spend long hours sitting or working on screens. Using a supportive chair, adjusting screen height to eye level, and taking frequent breaks can help reduce strain on the cervical spine and minimize discomfort. Additionally, stress management strategies such as practicing yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce muscle tension in the neck and shoulders, preventing chronic pain and dizziness. Implementing these lifestyle changes can significantly improve posture, spinal health, and overall well-being.
Exercises for Prevention and Ongoing Relief
Regular exercise plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy cervical spine and preventing recurring episodes of cervicogenic dizziness. Chiropractic care can help realign the cervical spine, improve joint mobility, and reduce nerve irritation, providing long-term relief from neck pain and headaches. Additionally, incorporating balance exercises into a daily routine enhances proprioceptive function, improving stability and reducing dizziness caused by proprioceptive dysfunction. Strengthening the deep neck muscles, scalene muscles, and multifidus can further support proper posture and prevent future occurrences of neck pain causing headache and dizziness.
Conclusion
Neck pain, headache, and dizziness often stem from issues within the cervical spine, affecting balance, posture, and nerve function. Conditions such as cervicogenic dizziness, cervical radiculopathy, and cervical myofascial pain syndrome can lead to long-term discomfort if left untreated. Seeking a board-certified pain specialist for a personalized treatment plan—including physical therapy, chiropractic care, and medical interventions—can help manage symptoms effectively.
FAQs
Why does my head and neck hurt, and I feel dizzy?
This could be due to cervicogenic dizziness, vertebral artery dissection, cervical osteoarthritis, or cervical stenosis, which impact blood flow and nerve function in the neck. In some cases, underlying conditions such as high blood pressure, dehydration, or an inner ear problem like vestibular neuritis could also contribute to these symptoms.
Should I go to urgent care for neck pain?
If your neck pain is sudden, severe, or accompanied by neurological disorder symptoms such as weakness, vision changes, or difficulty speaking, seek emergency medical care immediately. Additionally, if the pain follows a traumatic injury, such as a car accident or fall, or is associated with symptoms like numbness, tingling, or loss of coordination, it is best to consult a healthcare professional without delay.
What medication is good for neck and head pain?
Over-the-counter painkillers such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen may help. For chronic pain, muscle relaxers, triptans, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) inhibitors may be prescribed. By understanding the connection between neck pain, headache, and dizziness, individuals can take proactive steps toward effective treatment and long-term relief.


