Thank you for checking out the Articles from OrMobility Physical Therapy & Performance. We are Douglas County’s highest rated physical therapy clinic. Just check out our google reviews! People from Roseburg, Winchester, Winston, Green, and Sutherlin love our services. Now continue to our article to read more!
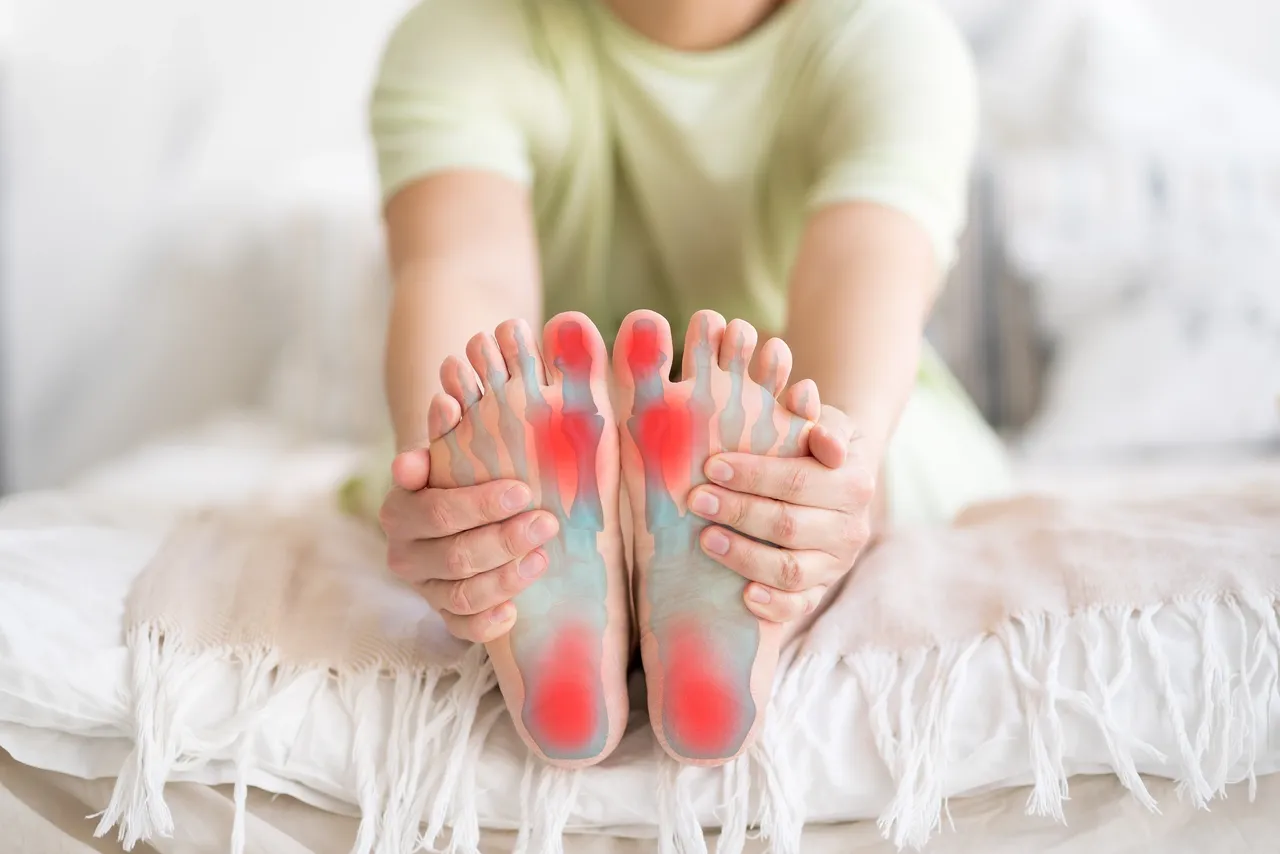
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by pain and inflammation in the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot from the heel to the toes. The plantar fascia acts as a shock absorber and supports the arch of the foot. When it becomes inflamed or irritated, it can cause a sharp, stabbing pain in the heel or arch of the foot.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is often caused by repetitive strain or overuse of the foot. This can be due to activities such as running, walking long distances, or standing for extended periods of time. It can also be caused by wearing shoes with poor arch support or high heels, which can put extra stress on the plantar fascia.
People who are overweight or obese are also at higher risk for developing plantar fasciitis, as the extra weight puts more pressure on the feet. Other factors that can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis include:
- Flat feet or high arches
- Tight calf muscles or Achilles tendon
- Poor foot mechanics or gait abnormalities
- Certain medical conditions, such as arthritis or diabetes
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
The main symptom of plantar fasciitis is pain in the heel or arch of the foot, which can be especially noticeable first thing in the morning or after sitting or standing for long periods of time. The pain may improve with activity, but can worsen again after prolonged use. Other symptoms may include:
- Swelling or redness in the affected area
- Stiffness or limited mobility in the foot
- Aching or burning sensation in the foot
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods of time
Diagnosis and Treatment
To diagnose plantar fasciitis, your doctor may perform a physical examination of your foot and ask about your symptoms and medical history. They may also order imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, to rule out other conditions that may be causing your foot pain.
Treatment for plantar fasciitis usually involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and pain management techniques. This may include:
- Resting the affected foot and avoiding activities that aggravate the condition
- Stretching exercises to improve flexibility and relieve tension in the plantar fascia
- Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support and cushioning
- Using orthotic inserts or heel cups to provide additional support and relieve pressure on the plantar fascia
- Applying ice or heat therapy to reduce pain and inflammation
- Taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and reduce inflammation
In some cases, more advanced treatments may be necessary, such as corticosteroid injections, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, or surgery. However, these are usually reserved for cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide relief.
Prevention
While plantar fasciitis can be a painful and debilitating condition, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing it. These may include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the feet
- Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support and cushioning
- Stretching your feet and calf muscles regularly, especially before and after exercise
- Avoiding activities that put excessive strain on your feet
- Getting treatment for foot or gait abnormalities, such as flat feet or high arches
- Using orthotic inserts or heel cups if you have a history of foot pain or injury
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. While it can be challenging to treat, there are many effective therapies available to help manage symptoms and promote