Introduction
Left shoulder pain is a common complaint that can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds. The shoulder joint is one of the most mobile and complex joints in the body, allowing for a wide range of movements. This complexity makes the shoulder susceptible to various injuries and conditions that can lead to pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for left shoulder pain is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the potential causes of left shoulder pain, common symptoms associated with different conditions, diagnostic approaches, and a variety of treatment options to alleviate discomfort and improve shoulder function.
Anatomy of the Left Shoulder
The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint that connects the upper arm bone (humerus) with the shoulder blade (scapula) and collarbone (clavicle). The joint is surrounded by a network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles that provide stability and allow for a wide range of movements, including lifting, reaching, and rotating the arm. The shoulder joint also comprises two smaller joints: the acromioclavicular (AC) joint, where the collarbone meets the shoulder blade, and the sternoclavicular (SC) joint, where the collarbone connects to the sternum.
Common Causes of Left Shoulder Pain
Left shoulder pain can result from various underlying causes, ranging from overuse injuries to medical conditions. Some common causes include:
Rotator Cuff Injuries:
The rotator cuff is a group of four tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and allowing for movement. Injuries to the rotator cuff, such as tears or strains, can occur due to overuse, trauma, or degeneration.
Shoulder Impingement:
Shoulder impingement occurs when the rotator cuff tendons or bursa (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joint) become irritated or inflamed, often due to repetitive overhead movements.
Bursitis:
Inflammation of the bursa can lead to bursitis, causing shoulder pain and limited range of motion.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis):
Frozen shoulder is a condition characterized by the thickening and tightening of the joint capsule, leading to pain and stiffness.
Osteoarthritis:
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that can affect the shoulder joint, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Tendinitis:
Tendinitis refers to inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder, commonly affecting the biceps or rotator cuff tendons.
Fractures and Dislocations:
Trauma or falls can result in fractures or dislocations of the bones in the shoulder, leading to acute left shoulder pain.
Nerve Impingement:
Compression or pinching of nerves in the shoulder region can cause pain, tingling, or weakness in the left shoulder and arm.
Referred Pain:
Pain originating from other areas, such as the neck or upper back, can be felt in the left shoulder, causing referred pain.
Symptoms Associated with Left Shoulder Pain

The symptoms of left shoulder pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms may include:
Pain:
Persistent or intermittent pain in the left shoulder, ranging from mild to severe.
Stiffness:
Feeling of tightness or reduced range of motion in the left shoulder joint.
Weakness:
Difficulty lifting or moving the left arm due to muscle weakness.
Clicking or Popping:
Audible or palpable clicking or popping sensations during shoulder movements.
Swelling:
Visible or palpable swelling around the left shoulder joint.
Limited Mobility:
Difficulty performing activities that require overhead movements or reaching across the body.
Numbness and Tingling:
Sensations of numbness, tingling, or burning in the left shoulder or arm.
Muscle Spasms:
Involuntary muscle contractions in the left shoulder region.
It is important to pay attention to the characteristics and patterns of shoulder pain to aid in diagnosing the underlying cause accurately.
Diagnosing Left Shoulder Pain
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management of left shoulder pain. Healthcare professionals use a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies to identify the cause of shoulder pain. Diagnostic methods may include:
Medical History:
A detailed history of symptoms, previous injuries, and medical conditions provides important clues for diagnosis.
Physical Examination:
A thorough examination of the left shoulder, including range of motion, strength testing, and palpation, helps identify areas of tenderness or instability.
Imaging Studies:
X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans can provide detailed images of the shoulder joint, helping identify fractures, dislocations, tears, or other structural abnormalities.
Electromyography (EMG):
EMG measures electrical activity in muscles and can help identify nerve impingement or muscle-related problems.
Diagnostic Injections:
In some cases, diagnostic injections of local anesthetics into specific structures can help pinpoint the source of pain.
Treatment Options for Left Shoulder Pain
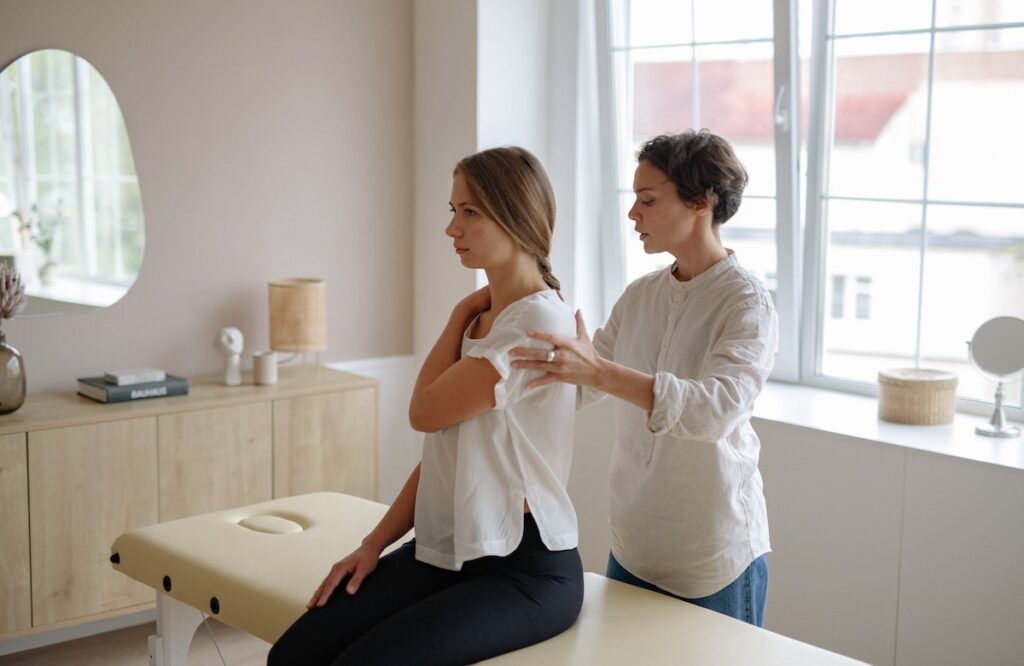

Treatment for left shoulder pain varies depending on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual health factors. Some common treatment options include:
Rest and Activity Modification:
Resting the left shoulder and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain can promote healing and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy exercises can improve shoulder strength, flexibility, and stability, aiding in recovery and preventing future injuries.
Pain Medications:
Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, NSAIDs) may provide temporary relief from shoulder pain and inflammation.
Cold and Heat Therapy:
Applying cold packs or warm compresses to the affected shoulder can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Steroid Injections:
Corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief for specific shoulder conditions.
Manual Therapy:
Chiropractic adjustments or osteopathic manipulations can help realign the shoulder joint and improve shoulder function.
Surgical Interventions:
In cases of severe injuries or conditions, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair torn tendons, ligaments, or fractures.
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments
Preventing left shoulder pain involves adopting healthy habits and making lifestyle adjustments, especially for individuals engaged in repetitive or strenuous activities. Some preventive measures include:
Proper Ergonomics:
Maintaining good posture and using ergonomic tools can reduce strain on the shoulder during work or daily activities.
Strengthening Exercises:
Regularly performing shoulder-strengthening exercises can help maintain shoulder stability and prevent injuries.
Warm-Up and Cool-Down:
Engaging in proper warm-up and cool-down routines before and after physical activities can reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Proper Lifting Technique:
Lifting heavy objects with the proper technique, using the legs and not the shoulders, can prevent strain on the shoulder muscles.
Avoid Overexertion:
Recognizing and avoiding activities that cause pain or discomfort can prevent overuse injuries.